

Other, more exotic states of matter can occur at extremely high energy levels or at extremely low temperatures, where atoms and molecules (or their components) arrange in unusual ways. Plasmas occur naturally in flames, lightning and auroras. This means that a plasma has very different properties from those of an ordinary gas. While it’s similar to a gas the electrons are free in a cloud rather than attached to individual atoms. Plasma is sometimes referred to as a fourth state of matter. The atoms and molecules move freely and spread apart from one another. They move around but stay close together. In a liquid, the atoms and molecules are loosely bonded. Liquids – definite volume but able to change shape by flowing.They vibrate in place but don’t move around. In a solid, the atoms and molecules are attached to each other. Solids – relatively rigid, definite volume and shape.
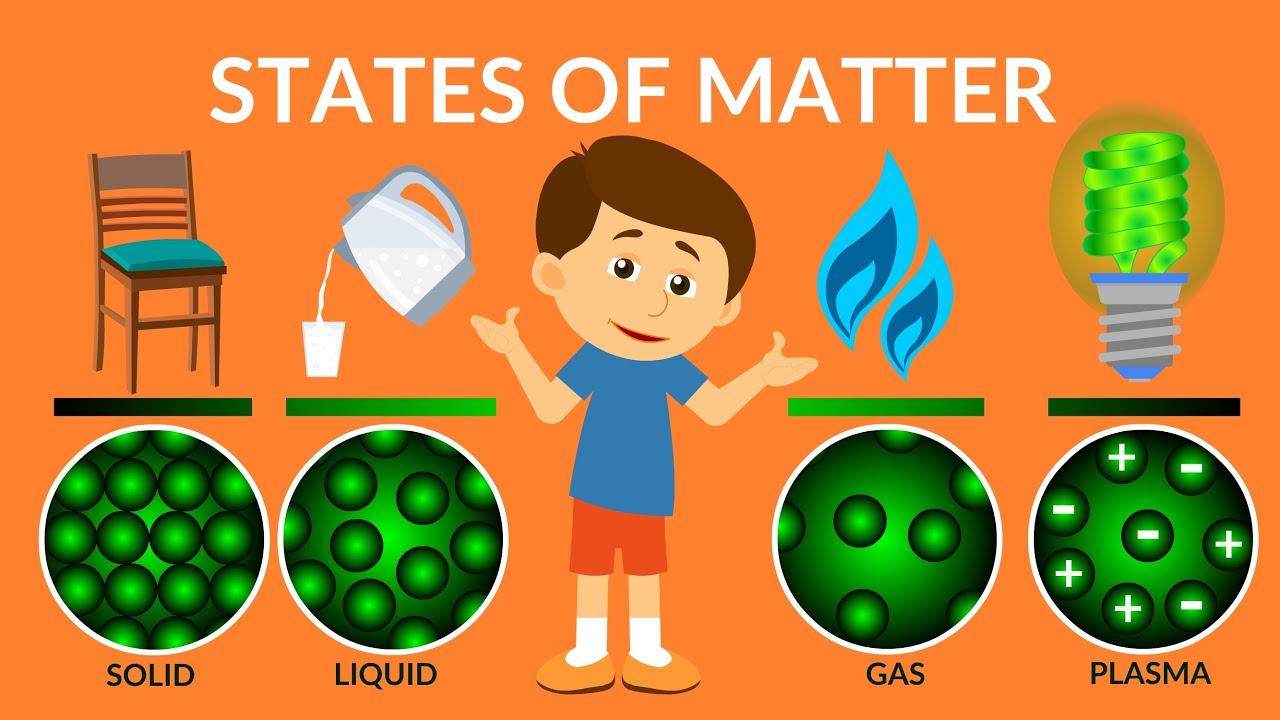
Investigate the properties of a non-Newtonian fluid.ĭescribe the general process of crystal formation.Ī “ state of matter” is a way to describe the behaviour of atoms and molecules in a substance. Understand how matter changes from one state to another and what affects the change.ĭescribe the processes of evaporation and condensation.ĭescribe the processes of melting and solidification.ĭescribe the processes of freezing and melting. Understand the transitions between states of matter. Differentiate between the three main states of matter.ĭescribe the properties of a solid, a liquid, and a gas.ĭescribe the properties of a solid and a liquid.ĭescribe the properties of gases and liquids.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
